Efficiency of uranium use (Sustainability Assessment)
This page is the "Appendix IV" to Environmental Impact from Depletion of Resources
This appendix presents examples of the end uses of uranium (normalized by energy delivered in GW·a) in a simple NES consisting of a nuclear power plant with an open (once through) uranium fuel cycle analysed with the NEST code described in Ref.[1].
Contents
Description of the nuclear energy system
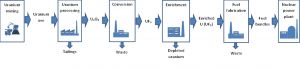
Figure 1 illustrates the mass flow of front end facilities of an NES starting with mining and ending with the nuclear power plant.
The characteristics of the individual nuclear fuel cycle facilities that are typical for a current NES with an open fuel cycle are presented in Table 1 (input data necessary for calculation).
| Front end fuel cycle stages and nuclear power plant operation | Parameter | Name | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mining and processing | U-235 concentration in natural isotopes blend (%/100) | εF | 0.00711 |
| Losses at extraction (%/100) | l1 | 0.20* | |
| Conversion | Losses (%/100) | l2 | 0.005 |
| Enrichment | U-235 concentration in fuel (%/100) | εP | 0.04 |
| U-235 concentration in depleted uranium (%/100) | εT | 0.0025 | |
| Losses (%/100) | l3 | 0 | |
| Fuel fabrication | Losses (%/100) | l4 | 0.01 |
| Nuclear power plant (energy conversion) | Unloaded fuel average burnup (MW·d/kg) | Q | 45 |
| Nuclear power plant net thermal efficiency (%/100) | η | 0.32 |
* - The lower margin of a range provided in Ref.[2] (20–35% depending on the technology) is used for this example. ‘0.20’ corresponds to open pit mining with conventional milling.
Material balance of the nuclear energy system
A detailed algorithm of the material balance calculation for different options of the fuel cycle, including
the front end of a once through fuel cycle is described in Appendix II of the INPRO methodology manual on
economics[1].
The equation describing the link between the mass of heavy metals at different stages of the front end of the
fuel cycle (HMk),
can be easily converted into a formula for the amount of natural uranium spent on the production of an
electricity unit. Here, HMIjj+1 is the quantity of heavy metal necessary at stage j to produce 1 kg of fuel at the next
stage (j+1) without accounting for losses (i.e. in an ‘ideal’ case); lj is the loss of uranium during processing at every
stage of the front end (e.g. j=2 losses at uranium conversion); all values are input data to NEST.
The equation estimating the amount of natural uranium necessary to produce 1 GW·a of electricity in a once
through fuel cycle (HM0) is the following:
where 365 × 103 is a coefficient converting GW·a into MW·d, and the rest of parameters are described in Table 1
(for simplicity, the first core fuel and reload fuel are not differentiated between here).
Numerical calculation based on the input data in Table 1 yields that approximately 2.5 × 105 kg of natural
uranium is necessary to produce 1 GW·a of electricity. For completeness, it should be mentioned that such a result
can be obtained not just by using NEST algorithms, and the INPRO assessors may use other tools, e.g. NFCSS
developed by the IAEA and available on the IAEA web site[3].
Thus, the NES retrieves 34.9 GW·h from 1 tU. This value of 34.9 GW·h/tU corresponds to the value of U0
defined in criterion CR1.4.
Sensitivity of the end use of uranium in the nuclear energy system
By looking at Table 1 (characteristics of NES facilities), it is obvious how the efficiency of the NES could
be increased: firstly by reducing the losses in the fuel cycle facilities, i.e. in the processing, conversion and fuel
fabrication facility, and by reducing the enrichment in the tailings of the enrichment facility, i.e. in the depleted
uranium; and secondly, by increasing the nuclear power plant’s thermal efficiency and average burnup of the
nuclear fuel to be unloaded.
In Table 2, the sensitivities of the characteristics of the NES fuel cycle facilities to increase the efficiency of
the uranium end use are presented. In the base case, the NES end use of natural uranium amounts to 251.1 tU to
generate 1 GW·a of electricity. Table 2 presents the change of the NES end use of uranium in the cases when the
losses of uranium in the fuel cycle facilities are decreased by 10% and 20%.
| Fuel cycle stages | Base case losses (%/100) | Reduction by 10% | Reduction by 20% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Losses (%/100) | Uranium end use (tU) | Reduction of U end use (tU) | Losses (%/100) | Uranium end use (tU) | Reduction of U end use (tU) | ||
| Processing | 0.20 | 0.18 | 247.0 | 4.1 | 0.16 | 242.8 | 8.3 |
| Conversion | 0.005 | 0.0045 | 251.0 | 0.1 | 0.004 | 250.9 | 0.2 |
| Enrichment | 0.0025 (tails assay) | 0.00225 | 239.8 | 11.3 | 0.002 | 229.6 | 21.5 |
| Fuel fabrication | 0.1 | 0.009 | 250.9 | 0.2 | 0.008 | 250.6 | 0.5 |
Table 3 presents the sensitivities of the characteristics of the nuclear power plant with regard to the end use of natural uranium. The influences of two characteristics are studied, namely, the thermal efficiency of the plant and the (core average) burnup of the nuclear fuel.
| Nuclear power plant parameter | Base case value | Increase by 10% | Increase by 20% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter value | Uranium end use (tU) | Reduction of uranium end use (tU) | Parameter value | Uranium end use (tU) | Reduction of uranium end use (tU) | ||
| Thermal efficiency | 0.32 %/100 | 0.352 %/100 | 228.3 | 22.8 | 22.8 0.384 %/100 | 209.3 | 41.8 |
| Average burnup | 45 MW·d/kg | 49.5 MW·d/kg | 228.3 | 22.8 | 54 MW·d/kg | 209.3 | 41.8 |
A comparison of the results in Table 1 with Table 2 indicates that the highest relative increase of efficiency (or reduction) of natural uranium end use in the NES can be achieved by an increase of thermal efficiency of the power plant or by an increase of burnup in the fuel followed by a reduction of the tails assay in the enrichment facility.
See also
[ + ] Assessment Methodology | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, INPRO Methodology for Sustainability Assessment of Nuclear Energy Systems: Economics, IAEA Nuclear Energy Series No. NG-T-4.4, IAEA, Vienna (2014).
- ↑ ORGANISATION FOR ECONOMIC CO-OPERATION AND DEVELOPMENT NUCLEAR ENERGY AGENCY, INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Uranium 2011: Resources, Production and Demand, (‘Red Book’), OECD/NEA, Paris (2012).
- ↑ INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY, Integrated Nuclear Fuel Cycle Information System (INFCIS), IAEA, Vienna (2012), [1]